30 Label The Scheme Of Glucose Catabolism
The stages of glucose breakdown can be divided into four distinct phases. Glucose can be used to synthesize glycogen and other storage fuels or broken down further to provide energy for metabolic processes a series of reactions collectively termed cellular respiration.
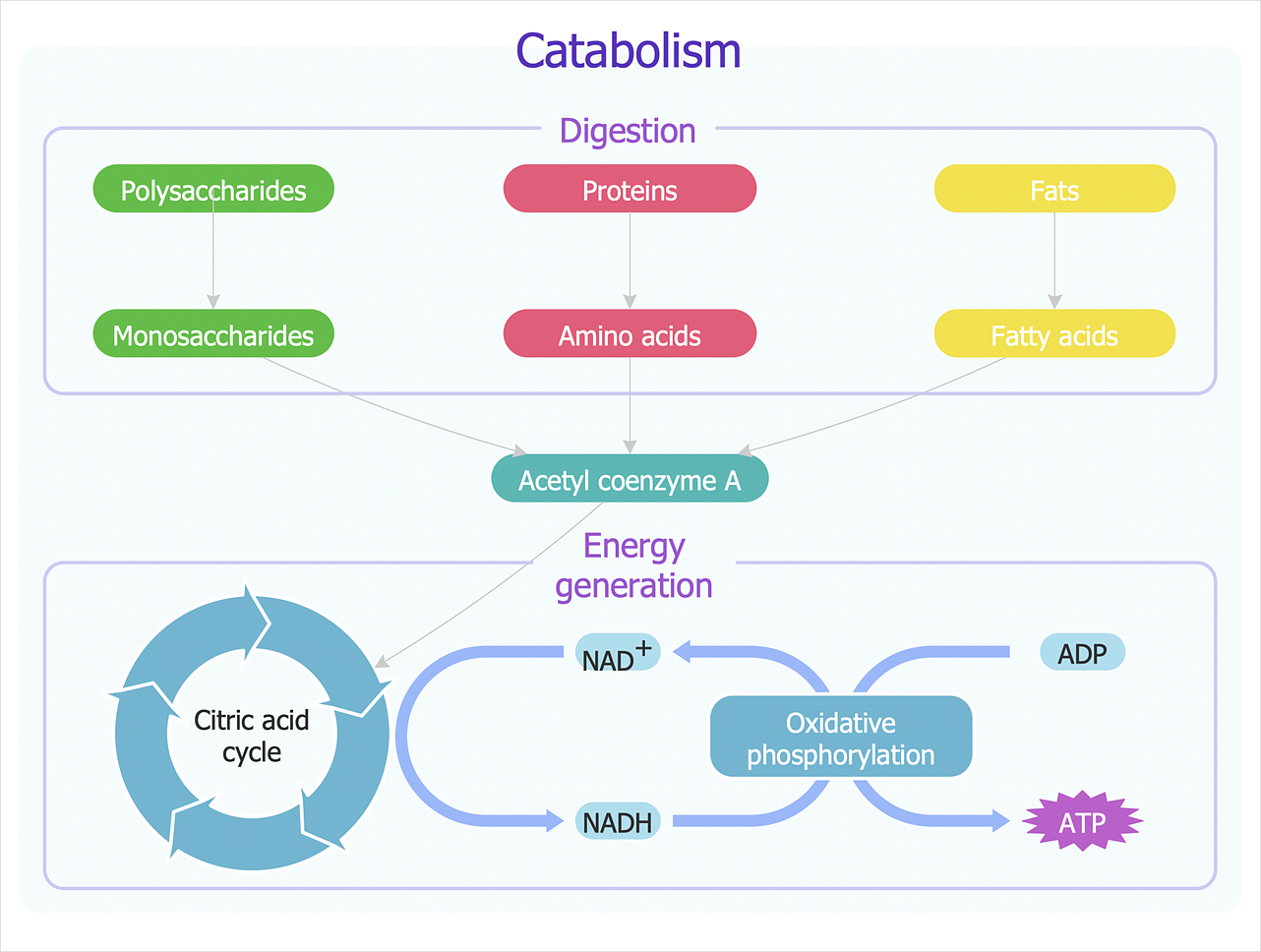 Catabolism Schematic Biochemical Diagram Glycolysis Overview
Catabolism Schematic Biochemical Diagram Glycolysis Overview
Energy is required to disrupt a substrates stable electron configuration.

Label the scheme of glucose catabolism. This process splits glucose in half and produces 2 atps for each glucose. During prolonged starvation the liver is the source of both glucose and the ketone bodies required by the brain to replace glucose. The glycolytic scheme yields as intermediate products of glucose catabo lism 2 molecules of pyruvate or lactate in which carbon atoms 1 2 and 3 correspond to glucose carbon atoms 3 and 4 2 and 5 1 and 6 respectively.
Experiments parallel to those with glucose have therefore been carried out. Part a scheme of glucose catabolism resp column. This process uses energy captured from electrons flowing to oxygen to produce most of the atps in cellular respiration.
Energy is required by an enzyme so that it can be reused. In the absence of oxygen pyruvate converts into either lactic acid lactic acid fermentation. Energy is needed for the enzyme to find its substrate.
Energy allows only the substrate to bind. In oxidation the electrons are stripped from a glucose molecule to reduce nad and fad. Digestion is the breakdown of carbohydrates to yield an energy rich compound called atp.
Glucose catabolism is defined as the breakdown of glucose molecule to provide energy to the cells in the form of atp adenosine triphosphate molecules. Please draw and label a diagram of the four stages of glucose catabolism resulting in atp synthesis in the presence of oxygen. The first and cytoplasmic portion of glucose catabolism in which glucose is converted in a series of linked enzyme catalyzed steps to pyruvic acid and useful chemical energy net gain 2 atps under anaerobic conditions or net gain 2 atps and 2 nadh2s under aerobic conditions.
This process splits glucose in half and produces 2 atps for each glucose. The liver uses glycolysis primarily as a source of biosynthetic intermediates with amino acid and fatty acid breakdown providing the majority of its fuel. Glycolysis acetyl coa krebs high energy electrons ferm colum.
Jump to navigation jump to search. The production of atp is achieved through the oxidation of glucose molecules. Techically either route is considered anaerobic because no molecular o2 is required in any of the steps.
In first step of glucose calabolism glucose is converted into pyruvate. Indicate the products and inputs of each stage and where there is substrate level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation of adp to form atp. This process produces some atp and carbon dioxide in the mitochondrion.
Pyruvic acid or derivative fermentation end products electron transport chain final electron acceptor.
 Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Requires Glyoxylate Shunt And Reverse
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Requires Glyoxylate Shunt And Reverse
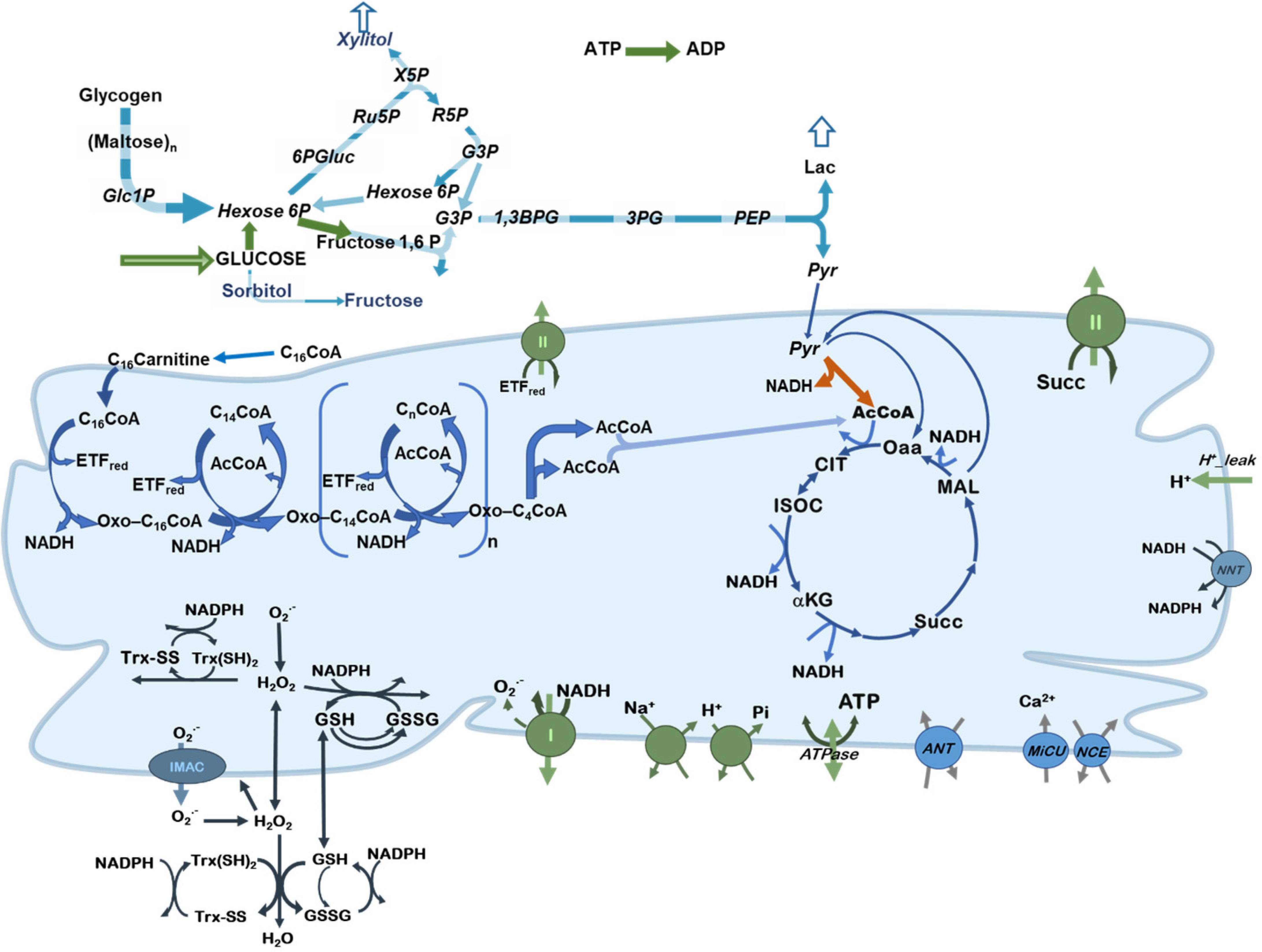 Frontiers Control And Regulation Of Substrate Selection In
Frontiers Control And Regulation Of Substrate Selection In
 Mitochondrial Lipoylation Integrates Age Associated Decline In
Mitochondrial Lipoylation Integrates Age Associated Decline In
 This Process Splits Glucose In Half And Produces 2 Atps For Each
This Process Splits Glucose In Half And Produces 2 Atps For Each
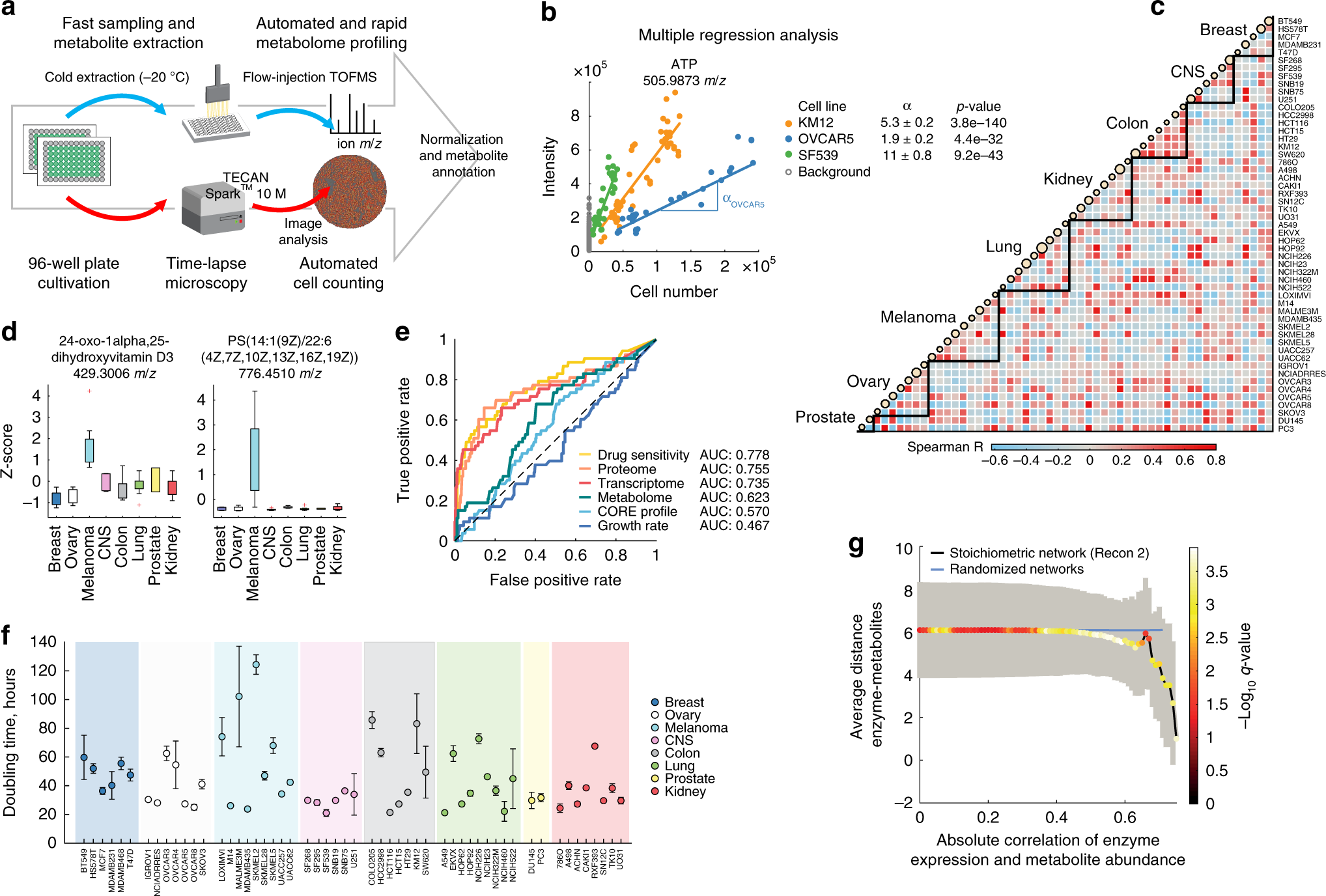 Metabolic Profiling Of Cancer Cells Reveals Genome Wide Crosstalk
Metabolic Profiling Of Cancer Cells Reveals Genome Wide Crosstalk
 Mapping Metabolic Changes By Noninvasive Multiparametric High
Mapping Metabolic Changes By Noninvasive Multiparametric High
 Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Requires Glyoxylate Shunt And Reverse
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Requires Glyoxylate Shunt And Reverse
Deletion Of Transketolase Triggers A Stringent Metabolic Response
 The Dynamic Side Of The Warburg Effect F1000research
The Dynamic Side Of The Warburg Effect F1000research
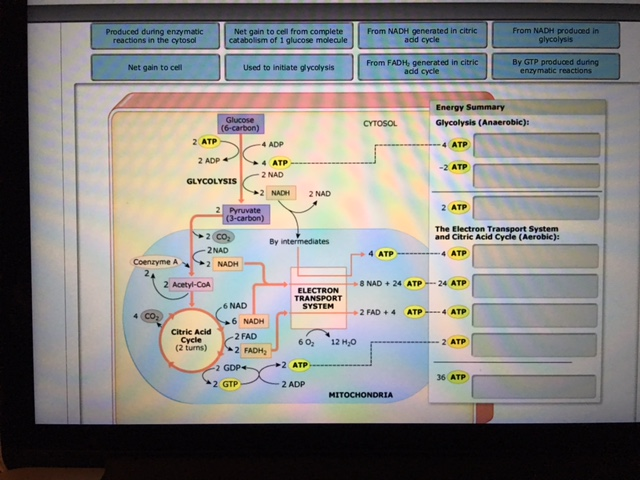 Solved Drag The Labels Onto The Diagram To Identify The P
Solved Drag The Labels Onto The Diagram To Identify The P
 Transfer Of 13 C Label Into Tyrosine And Its Precursors Transfer
Transfer Of 13 C Label Into Tyrosine And Its Precursors Transfer
 Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Requires Glyoxylate Shunt And Reverse
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Requires Glyoxylate Shunt And Reverse
 The Small Intestine Converts Dietary Fructose Into Glucose And
The Small Intestine Converts Dietary Fructose Into Glucose And
 General Concepts Of Etc And Oxidative Phosphorylation 1 Occurs
General Concepts Of Etc And Oxidative Phosphorylation 1 Occurs
 De Novo Acetate Production Is Coupled To Central Carbon Metabolism
De Novo Acetate Production Is Coupled To Central Carbon Metabolism
 Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Requires Glyoxylate Shunt And Reverse
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Requires Glyoxylate Shunt And Reverse
 Temporal Fluxomics Reveals Oscillations In Tca Cycle Flux
Temporal Fluxomics Reveals Oscillations In Tca Cycle Flux
 The Dynamic Side Of The Warburg Effect F1000research
The Dynamic Side Of The Warburg Effect F1000research
 Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Requires Glyoxylate Shunt And Reverse
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Requires Glyoxylate Shunt And Reverse
 Mva And Mep Pathway Specific Labeling Pattern Of Isoprene Units
Mva And Mep Pathway Specific Labeling Pattern Of Isoprene Units
 Chapter 5 Pearson Flashcards Quizlet
Chapter 5 Pearson Flashcards Quizlet
 Recent Advances In Mapping Environmental Microbial Metabolisms
Recent Advances In Mapping Environmental Microbial Metabolisms
 Glucose Catabolism Through Glycolysis Download Scientific Diagram
Glucose Catabolism Through Glycolysis Download Scientific Diagram
 Bc Ch 15 Glucose Catabolism Flashcards Quizlet
Bc Ch 15 Glucose Catabolism Flashcards Quizlet
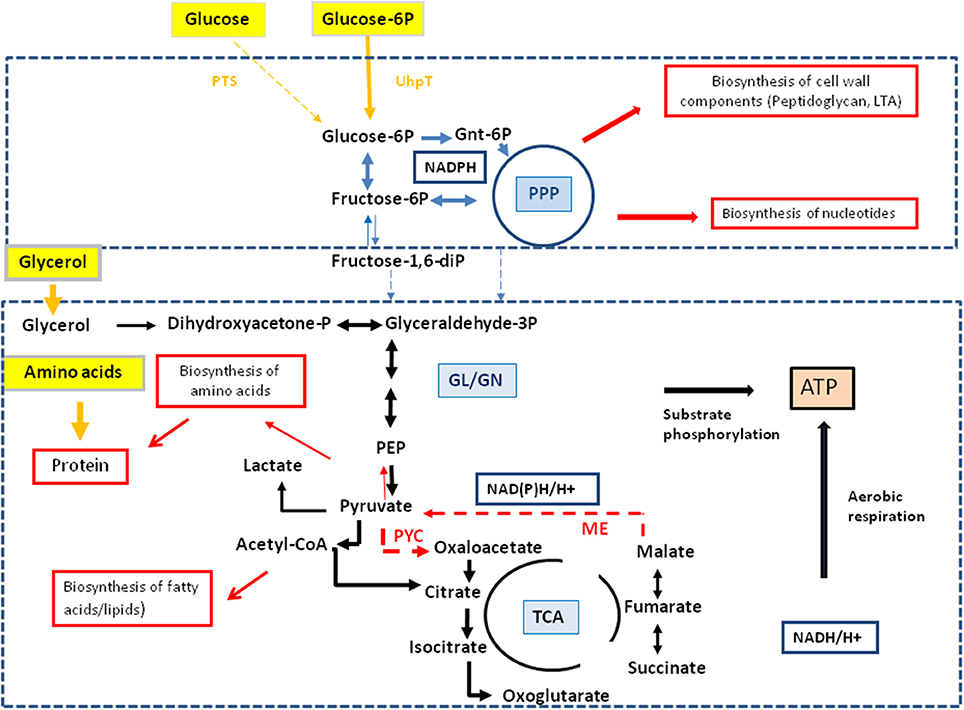 Frontiers Analysis Of Carbon Substrates Used By Listeria
Frontiers Analysis Of Carbon Substrates Used By Listeria
Effect Of Oxygen On Glucose Metabolism Utilization Of Lactate In
Post a Comment for "30 Label The Scheme Of Glucose Catabolism"