31 Draw And Label A Diagram That Explains The Doppler Effect
Draw and label a diagram that explains the doppler effect. In the diagram below you can also see how transverse waves form crests and troughs.
 Resonant Doppler Effect In Systems With Variable Delay
Resonant Doppler Effect In Systems With Variable Delay
Draw and label a diagram of the layers of the atmosphere.
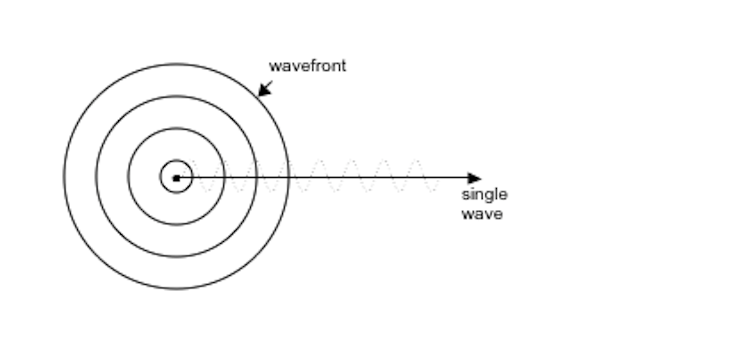
Draw and label a diagram that explains the doppler effect. Our world is replete with events and daily life experiences that are associated with doppler effect. It can be experienced with sound and light waves. Start studying project 4.
In which layer does all the weather occur. Explain in detail the doppler effect. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
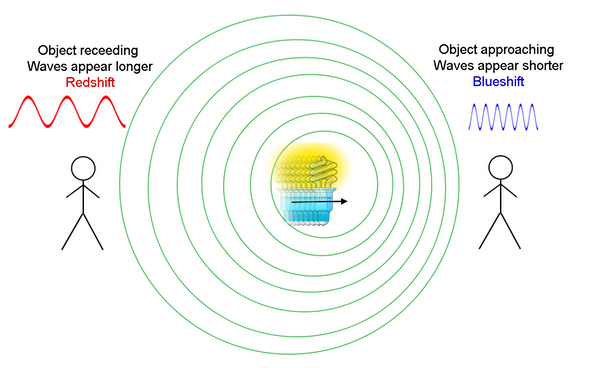
The doppler effect and sonic booms. Explain the red shift doppler effect and how it provides evidence for an expanding universe. The doppler effect states as a wave approaches an observer encounters waves with a higher frequency.
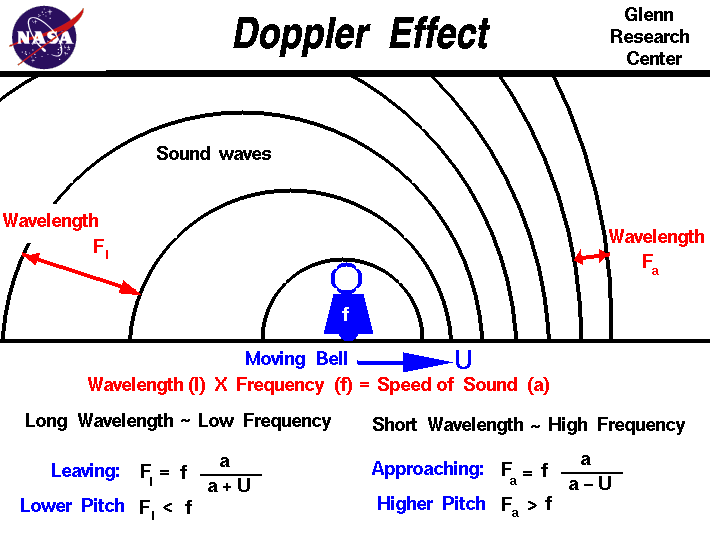
The doppler effect is a shift in the apparent or observed frequency and not a shift in the actual frequency at which the source vibrates. Like many other phenomena the doppler effect is named after a scientist christian doppler who is credited with its discovery. This physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the doppler effect of moving sound waves.
It explains how to solve doppler effect problems in physics. Think critically why would a passing car exhibit a greater sound frequency change when it moves at 30 ms than when it moves at 12 ms. The sudden change in pitch of a car horn as a car passes by source motion or in the pitch of a boom box on the sidewalk as you drive by in your car observer motion was first explained in 1842 by christian doppler.
As the wave source moves away an observer encounters waves with a lower frequency. Lets see a bit more about what the doppler effect actually is. But light and sound also travel as waves.
His doppler effect is the shift in frequency and wavelength of waves which results from a source moving with respect to the medium a receiver. A light wave like a water wave is an example of a transverse wave which causes a disturbance in a medium perpendicular to the direction of the advancing wave. As the source moves away from an observer the observer seeshears a lower frequency wave than the source actually is emitting.
Amplitude doppler effect states that when a wave moves towards an observer the wavelength will decrease when a wave moves away from an observer its wavelength will increase gets longer. Shock waves and sonic booms. The doppler effect is observed whenever the speed of the source is moving slower than the speed of the waves.
Doppler effect as the source of a wave sound or light approaches an observer the observer seeshears a higher frequency than the source actually is emitting.
 Ultrasound Book Chapter Iopscience
Ultrasound Book Chapter Iopscience
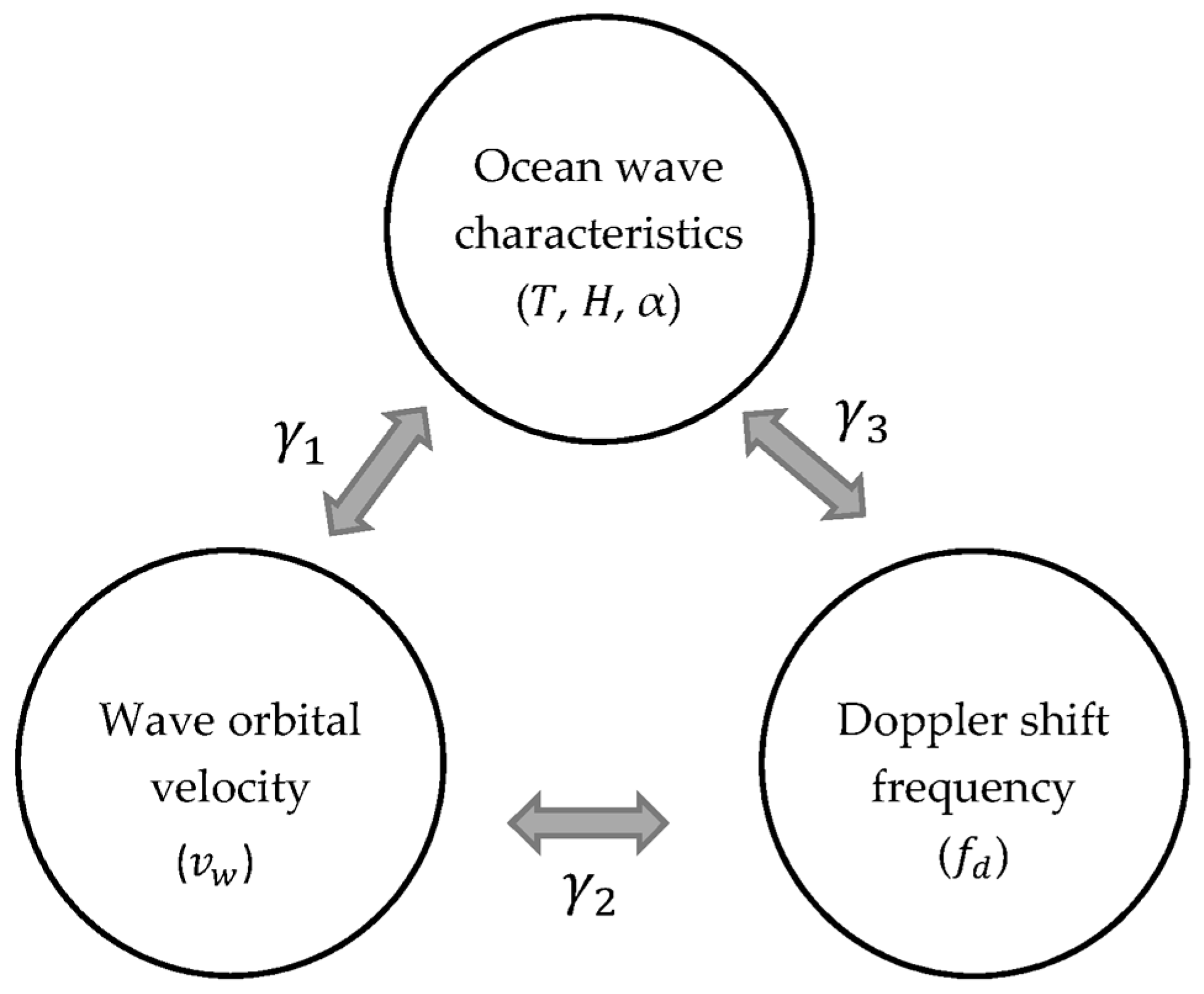 Remote Sensing Free Full Text Ocean Wave Measurement Using
Remote Sensing Free Full Text Ocean Wave Measurement Using
 Using Doppler Shifts Of Gps Signals To Measure Angular Speed
Using Doppler Shifts Of Gps Signals To Measure Angular Speed
Physics Tutorial The Doppler Effect
 Dopplereffect Hashtag On Twitter
Dopplereffect Hashtag On Twitter
 Scattering And Diffraction Springerlink
Scattering And Diffraction Springerlink
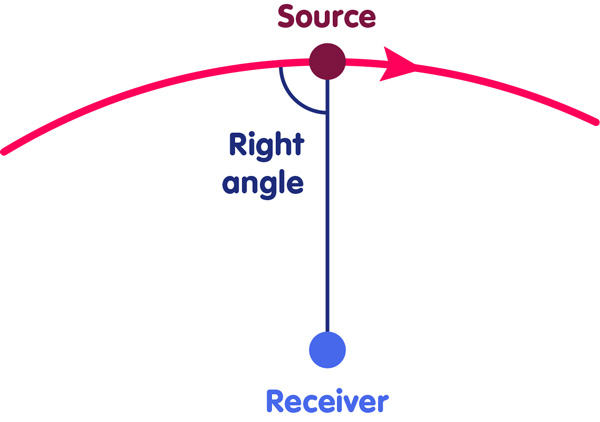 Waves Motion And Frequency The Doppler Effect Einstein Online
Waves Motion And Frequency The Doppler Effect Einstein Online
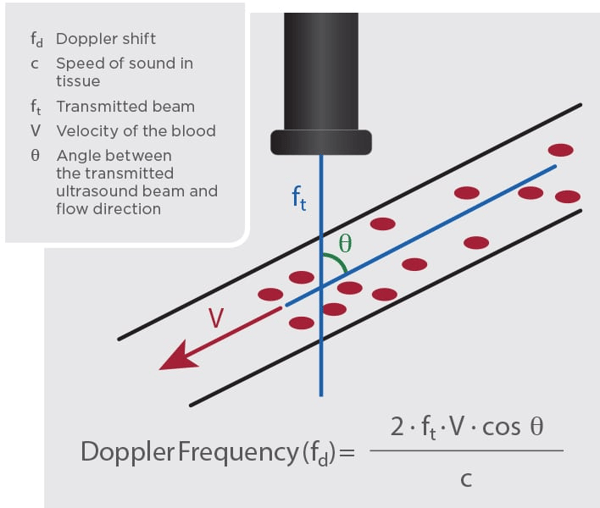 Span Id Hs Cos Wrapper Name Class Hs Cos Wrapper
Span Id Hs Cos Wrapper Name Class Hs Cos Wrapper
 Doppler Shift For Sound And Light
Doppler Shift For Sound And Light
 Doppler Effect Wavefront Diagrams And Word Problems Practice
Doppler Effect Wavefront Diagrams And Word Problems Practice
 Schematic View Of The Doppler Shift Of A Prograde Rotating Planet
Schematic View Of The Doppler Shift Of A Prograde Rotating Planet
 Wave Parameters Wavelength Amplitude Period Frequency Amp Speed
Wave Parameters Wavelength Amplitude Period Frequency Amp Speed
 Light Reflection And Refraction Britannica
Light Reflection And Refraction Britannica
 Recoil Induced Ultrafast Molecular Rotation Probed By Dynamical
Recoil Induced Ultrafast Molecular Rotation Probed By Dynamical
 Pdf Experiment And Theory The Case Of The Doppler Effect For
Pdf Experiment And Theory The Case Of The Doppler Effect For
 Measurement Of The Earth S Rotational Speed Via Doppler Shift Of
Measurement Of The Earth S Rotational Speed Via Doppler Shift Of
 Laser Doppler Flowmetry Springerlink
Laser Doppler Flowmetry Springerlink
 Recoil Induced Ultrafast Molecular Rotation Probed By Dynamical
Recoil Induced Ultrafast Molecular Rotation Probed By Dynamical
 Real Space Schematic Demonstration Of Various Doppler Effects Of
Real Space Schematic Demonstration Of Various Doppler Effects Of
 Force On A Moving Charge In A Magnetic Field Examples And
Force On A Moving Charge In A Magnetic Field Examples And
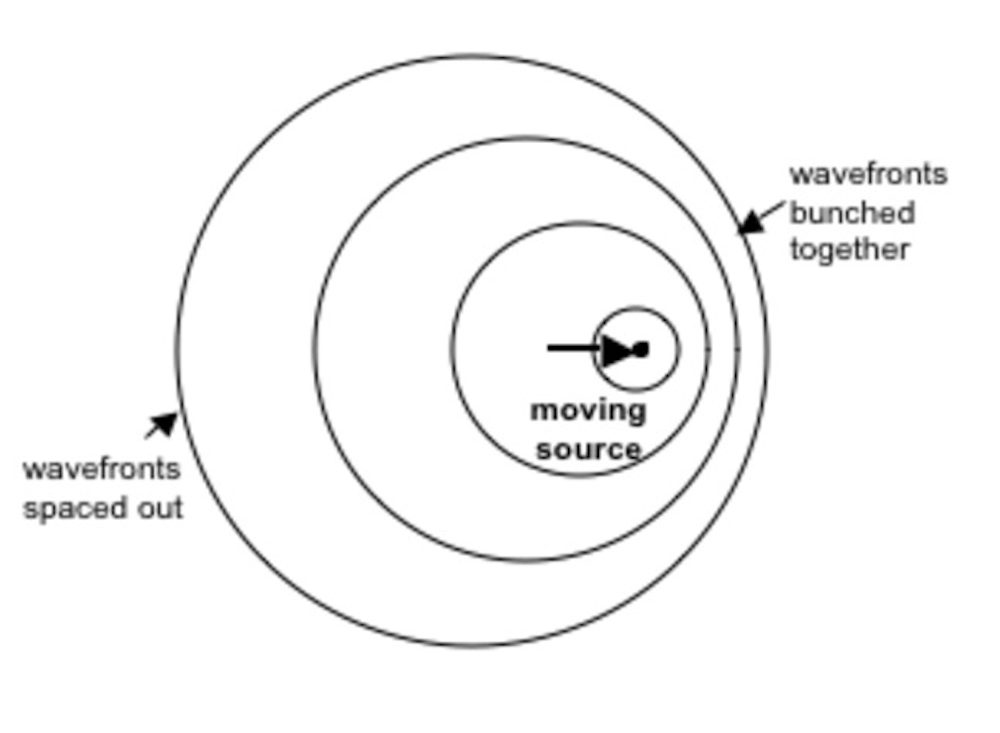




Post a Comment for "31 Draw And Label A Diagram That Explains The Doppler Effect"